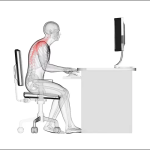
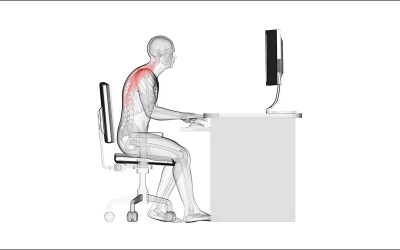
With so many individuals spending so much time at their desks, the number of people experiencing severe neck discomfort and dysfunction is also rising. If people were to set up their desk area in a way that encourages and supports excellent posture, and if they were also adamant about keeping these appropriate natural postures, it becomes easy to avoid these musculoskeletal disorders.
Workplace Ergonomics
Ergonomics is the process of creating tasks, workspaces, systems, and products more suited to the users’ needs is known as ergonomics.Ergonomics’ primary objective is to make work safer and more enjoyable by lowering the possibility of accidents and pain at work. It frequently entails introducing ergonomic solutions, such as better seating or workstations, in various workplace settings.
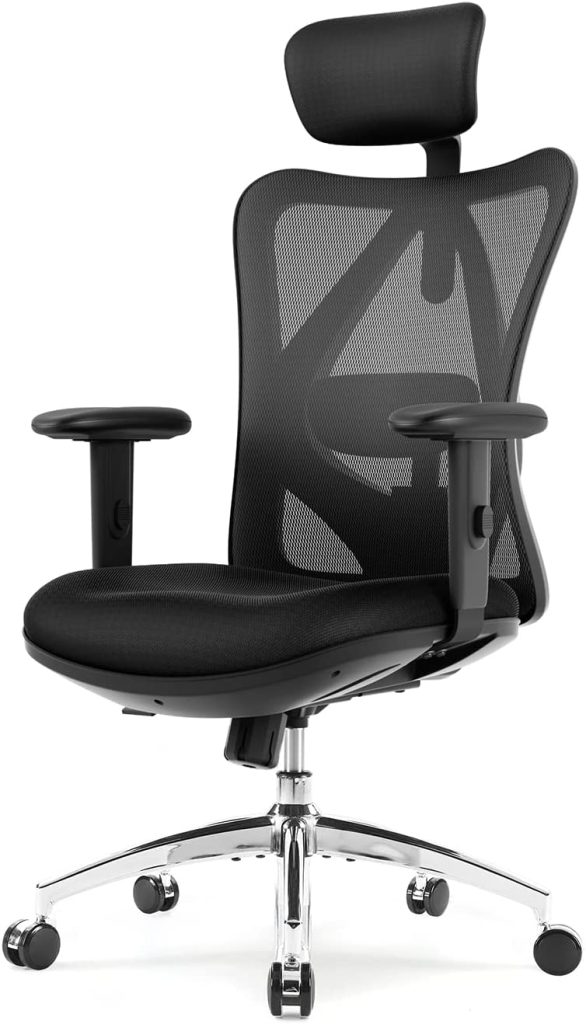
So, an ergonomic chair intends to optimize convenience, productivity, and efficiency. The science of ergonomics served as the inspiration for the design of this kind of chair. An ergonomic chair, for instance, considers the physical stresses the human body experiences while sitting and seeks to prevent them by supporting the body in all the appropriate locations.
Poor posture strains the muscles and ligaments that support your neck. It may result from having your head extended forward in front of your body. It is known as “tech neck,” and it affects people who spend their entire day staring at displays or using their phones. Sitting at your desk for more than eight hours a day may cause your shoulders may sag or round, which is another sign of poor posture.
Office chair-related neck pain
Office workers often get neck problems caused by their jobs, particularly those who use computers frequently. There is an acknowledgment that the genesis of neck diseases connected to the workplace is multifaceted and impacted by a wide range of individual, physical, and psychosocial factors.
Individual factors:
Gender, age, height, weight, body mass index, formal learning, smoking, sleeping habits, and free time were the following personal characteristics.
Physical factors:
Longevity of employment (years at the present workplace, hours a week, days a week), physical tiredness at the end of the day, physical workload (postures, motions, and pressures impacting the neck region), computer use, breaks at work, and climatic circumstances are all factors connected to the workplace (noise, lack of fresh air, dry air, changes of temperature, stench).
Psychosocial elements:
associated with the workplace include job pressure, work variety, and job happiness.
A quality ergonomics office chair helps in mitigating the effect of these factors.
Qualities of an ergonomic office chair:
Seat depth and breadth adjustments: How much support your thighs get depends on how deep your chair is adjusted. Sit back in your chair as far as you can to gauge the depth of your seat. There must be about three fingers’ width of space between your chair and behind your knees. An ergonomic chair will feature a seat slider.
Seat height adjustment:
A gas lift will be included on an ergonomic chair so you can change the height at which you are sitting. The ideal elevation is when your forearms are parallel to the surface of your desk; if your feet do not stay flat on the ground in this posture, you will require a footrest.
Seat Cushioning:
The backrest and seat cushion cushioning ought to be:
Thick enough to sustain prolonged sitting,
Soft enough to shield your pelvis from undue strain.
Made of a porous material.
It won’t be comfy after a few hours if it doesn’t feel comfortable when you first sit on it.
Wheels:
Find a chair with soft rubber wheels if you have a hard surface. Choose firm wheels if the carpet at your job or home office will improve your navigation.
Headrest:
reduces tension in the shoulders and upper torso by supporting the back of the head and the upper neck.
Armrests:
allow the shoulders to relax and aid in easing upper-body strain. However, using armrests when typing restricts wrist movement, which causes strains of forearm muscles.
Backrest Lumbar Support:
A vital feature of an ergonomic office chair supports your lower back. Ergonomic chairs support the spine’s natural “S” shape, reducing pressure on the backbone and pelvis and eliminating drooping. Customers can alter the backrest so that the curvature of the chair matches the curve of their spine for the best support.
Backrest recline:
A modifiable backrest permits a more personalized setup because you can alter it to maintain the natural alignment of your spine. If you utilize this feature all day, the backrest can sustain your upper body, lessening the stress on your muscles and spinal disks.
Here are some ergonomics seats you can shop for:
Home Office Desk Chairs with 5-Year Warranty
Ergonomic Office Chair, FelixKing Home Office Rolling Swivel Chair
Benefits of ergonomic office chairs
Be more productive
When you sit at your desk and work, you are investing in your future. Whether it’s a salary or projects that are in development, you will reap the benefits of your desk-work in the near, mid, and far future. This work deserves your attention, so you should be able to work without having to change locations often, get stiff muscles, or trigger chronic neck pain.
Better posture:
Ergonomic seats provide body support, promote good posture, and lessen pain.
Put your joints in a natural position and support your spine.
Align your shoulders, spine, and hips.
Because they are so adjustable, ergonomic chairs can support any body type. Ergonomic seats are accessible to all.
Increased productivity: Distractions from your pain at work can make it difficult to focus on your work. Being at ease increases your likelihood of focusing better and accomplishing superior work.
Conclusion
You will have the best chance of maintaining good posture if you sit in a comfortable ergonomic chair adjusted for you. An ergonomically built chair considers factors like posture, comfort, support, and health to provide the best possible support for the human body.